This module defines global parameters and general-level computational utilities. More...
Data Types | |
| type | stomach_emptying_pattern |
| A data structure that defines the stomach emptying pattern as dependent on the temperature and the fish mass. More... | |
| interface | cum2rate |
Public interface for the cum2rate function that calculates rate from raw cumulative array. Note that rate unit time is defined by the integer rate_unit argument (as default, per commondata::minute). For details see cum2rate_int() and cum2rate_r(). More... | |
| interface | add_to_history |
Simple history stack function, add to the end of the stack. We need only to add components on top (end) of the stack and retain HISTORY_SIZE_SPATIAL elements of the prior history (for a spatial moving object). The stack works as follows, assuming 100 and 200 are added: [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10] [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 100] [3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 100 200]. More... | |
| interface | last |
| Return the last element of a history array with optional offset. More... | |
| interface | oxygen_rate_std |
| Function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the curve from Fig. 9 in Evans, D.O. (1990) Metabolic Thermal compensation by rainbow trout: effects on standard metabolic rate and potential usable power. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 585–600. More... | |
| interface | sgr |
| Function for calculating specific growth rate. More... | |
| interface | within |
| Force a value within the range set by the vmin and vmax dummy parameter values. More... | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | |
| Definition of time plot scale types for ::global_time_plots_unit_scale. More... | |
Functions/Subroutines | |
| impure character(len=:) function, allocatable | model_parameters_txt () |
| Produce a text string containing all global parameters of the model. More... | |
| pure logical function | is_stress () |
| Calculate if stress factor grid is enabled. Stress is disabled if any of the stress parameters are not defined; this includes the stress suppression grid array or the stress intervention array. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | logistic (X, A, C, R) |
| Logistic function is defined by the equation. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | michaelis_menten (x, r_max, x50) |
| Michaelis-Meneten function: More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | midgut_temp_factor (temperature) |
| Calculate temperature adjustment factor for the Michaelis-Menten absorption process in the midgut. The function is based on the cubic spline approcimation using the grid vectors defined by commondata::global_temp_factor_midgut_t and commondata::global_temp_factor_midgut_t. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | feed_energy (feed_mass, gross_energy, is_adjust_water_uptake, water_uptake) |
| Calculate the energy content of a feed mass. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | energy_o2 (l_o2) |
| Calculate the enegretic equivalent (kJ) of Oxygen uptake (l O2) Source: Rønnestad B291. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | o2mass (vol_l) |
| Calculate the mass of 1 dm3 (l) of Oxygen. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | o2vol (mass_g) |
| Calculate the volume of 1 dm3 (l) of oxygen. More... | |
| elemental integer(long) function | rate2int (rate_min) |
| The function converts rate per min to interval in seconds. More... | |
| pure real(srp) function, dimension(:), allocatable | cum2rate_int (inarray, rate_unit) |
| Given an in put array of cumulative sum, this function calculates the rate per unit time defined by the rate_unit argument (as default, per commondata::minute). This requires working on the appropriate difference values for each time interval. Note: This function version accepts integer array. More... | |
| pure real(srp) function, dimension(:), allocatable | cum2rate_r (inarray, rate_unit) |
| Given an in put array of cumulative sum, this function calculates the rate per unit time defined by the rate_unit argument (as default, per commondata::minute). This requires working on the appropriate difference values for each time interval. Note: This function version accepts real array (::srp). More... | |
| pure real(srp) function, dimension(:), allocatable | blockrate (inarray, rate_unit) |
| Calculate rate based on simple block data, only the block start and end values are considered. More... | |
| pure real(srp) function, dimension(:), allocatable, private | sgr_blockrate (inarray, rate_unit, time_unit) |
| Calculate an array of specific growth rate rate values based on simple block data,. More... | |
| pure subroutine, private | add_to_history_i4 (history_array, add_this) |
Simple history stack function, add to the end of the stack. We need only to add components on top of the stack and retain commondata::history_size_spatial elements of the prior history (for a spatial moving object). The stack works as follows, assuming 100 and 200 are added: [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]; [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 100]; [3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 100 200]. More... | |
| pure subroutine, private | add_to_history_r (history_array, add_this) |
Simple history stack function, add to the end of the stack. We need only to add components on top of the stack and retain commondata::history_size_spatial elements of the prior history (for a spatial moving object). More... | |
| pure subroutine, private | add_to_history_char (history_array, add_this) |
Simple history stack function, add to the end of the stack. We need only to add components on top of the stack and retain commondata::history_size_spatial elements of the prior history. More... | |
| pure real(srp) function, private | last_in_history_r (history_array, offset) |
Return the last value in the array. Note that this function is especially useful for long nested objects, to avoid complex set. More... | |
| pure integer function, private | last_in_history_i4 (history_array, offset) |
Return the last value in the array. Note that this function is especially useful for long nested objects, to avoid complex set. More... | |
| pure character(len=:) function, allocatable, private | last_in_history_char (history_array, offset) |
Return the last value in the array. Note that this function is especially useful for long nested objects, to avoid complex set. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function, private | within_r (value_in, vmin, vmax) |
| Force a value within the range set by the vmin and vmax dummy parameter values. If the value is within the range, it does not change, if it falls outside, the output force value is obtained as min( max( value, FORCE_MIN ), FORCE_MAX ) More... | |
| elemental integer function, private | within_i (value_in, vmin, vmax) |
| Force a value within the range set by the vmin and vmax dummy parameter values. If the value is within the range, it does not change, if it falls outside, the output force value is obtained as min( max( value, FORCE_MIN ), FORCE_MAX ) More... | |
| pure real(srp) function, dimension(:), allocatable, private | oxygen_rate_std_spline (temperature) |
| Function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the empirical curve defined by interpolation on the grid determined by two global arrays: More... | |
| pure real(srp) function, private | oxygen_rate_std_ddpi (temperature) |
| Function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the empirical curve defined by interpolation on the grid determined by two global arrays: More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | fcr (input_f, output_m) |
| Function to calculate the FCR, feed conversion rate | |
| elemental real(srp) function | kg2g (kg) |
| Convert kg to g. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | g2kg (g) |
| Convert g to kg. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | kg2mg (kg) |
| Convert kg to mg. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | mg2kg (mg) |
| Convert mg to kg. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | mg2g (mg) |
| Convert mg to g. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | g2mg (g) |
| Convert g to mg. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function | from_micro (mu_unit) |
| Convert micro (\mu) unit to unit, e.g. from micro mol to mol Metric prefix micro = 10^-6: unit x 0.000 001. More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function, private | sgr_r (weight1, weight2, time1, time2) |
| Calculates specific growth rate following Houde & Schekter (1981): More... | |
| elemental real(srp) function, private | sgr_i (weight1, weight2, time1, time2, time_unit) |
| Calculates specific growth rate following Houde & Schekter (1981): More... | |
| pure type(stomach_emptying_pattern) function | stomach_emptying_def_default () |
| Define the default stomach emptying data structure ::stomach_emptying_pattern in case the input data from a CSV file are absent. More... | |
| impure character(len=:) function, allocatable | stomach_emptying_txt (is_raw_s) |
| Show the stomach emptying data structure. More... | |
| impure character(len=:) function, allocatable | stomach_transport_txt (adjust, format, show, prefix) |
| Produce a formatted text string containing the adjusted stomach transport arrays commondata::global_transport_pattern_r and commondata::global_transport_pattern_t. More... | |
Variables | |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | svn_version_global = '0.1_o' |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | program_title = "FishMet: the fish appetite and feeding model" |
| Program title that appears on the main interface/window. More... | |
| logical, parameter, public | is_debug = .TRUE. |
| Logical flag that sets the DEBUG mode. When the program is running in the DEBUG mode, additional checks are done and more output is produced. More... | |
| logical, parameter, public | is_stress_enable = .TRUE. |
| Compile-time logical flag that defines if stress effects described by global_stress_factor_hour, global_stress_fact_suppress and global_stress_cost_smr. More... | |
| real(srp), parameter, public | debug_warn_level = 0.75_SRP |
| Warning level in the debugging mode. More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | label_len = 24 |
| The default length of labels and similar text strings. More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | file_name_len = 255 |
| The default length of the file name. More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | minimum_filename_chars = 7 |
| The minimum length of a data file. Note that cancelled file name dialog returns a six-char random sequence. Hence the minimum file name > 7. More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | hour =3600 |
| Global time constants, number of sec in hour and min. More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | minute =60 |
| integer, parameter, public | max_points_plot = 1000 |
| The maximum number of data points that are plotted for the model output arrays (squeezed arrays). More... | |
| logical, parameter, public | is_progress_bar_gui = .TRUE. |
| Global parameter defining if progress bar is printed in the GUI mode. More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | gui_progress_bar_max = 100 |
| Maximum value (steps) in the progress bar (minimum is 0) More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | gui_progress_bar_steps = 100 |
| Number of steps in the progress bar at the GUI mode. More... | |
| character(len=1), parameter, public | prog_bar_char = "#" |
| The symbol used for writing the progress bar in text mode. More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | prog_bar_len = 42 |
| The length of the progress bar in text mode. More... | |
| character, parameter, public | crlf = char(10) |
| integer(long), public | global_time_step |
| Global variable that defines the current time step. More... | |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | output_arrays_csv_file = "model_output_arrays" |
| Default file base-name for saving model output arrays. More... | |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | output_rate_data_csv_file = "model_rate_data" |
| Default file base-name for saving model rate data. More... | |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | output_dest_dir = "" |
| Default output directory: all plot and data file will be saved into this directory by default (local directory) unless reconfigured via commondata::global_output_dest. More... | |
| character(len=file_name_len), public | global_output_dest |
Output directory: all plot and output files will be saved into this directory, default value is set by output_dest_dir. Specifically, the following outputs are saved to the output_dest directory: More... | |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | param_file_name_def = "parameters.cfg" |
Defines the name of the file that keeps global parameters. The parameter file contains the coupled pairs of the parameter name and its value. Comments can be added, normally separated by the # commet symbol. More... | |
| character(len=file_name_len), public | global_param_file_name |
Defines the name of the file that keeps global parameters. This name is normally defined by the environment variable FFA_MODEL_PARAMETER_FILE that is processed in runtime::system_init(). If this environment variable is not set, the parameter file name is defined by the default param_file_name_def. More... | |
| integer, parameter, public | max_food_items_index = 4000 |
| Maximum number of food items in the fish stomach, this is the maximum index for the food items array in the_fish::stomach object. More... | |
| logical, public | verbose |
| Global logical flag to suppress extra text diagnostics and messages, the "quiet mode" or the "verbose mode". If the parameter is TRUE, then verbose mode is activated. More... | |
| @, public | scale_sec |
| @, public | scale_min |
| @, public | scale_hour |
| @, public | unscaled |
| integer, public | global_rate_interval |
| Default rate discretization interval in minutes, this interval is used to plot the ingestion rate. More... | |
| integer, public | global_run_model_hours |
| Default duration of the model run in hours. Note that parameter file uses hours as unit. Conversion to time steps is done in simulate::total_timesteps(). More... | |
| integer, public | global_day_starts_hour |
| Default hour at which the "daytime" is normally started. This means, in particular, that at the start of the simulation day starts with the offset equal to this parameter value. More... | |
| integer, public | global_run_model_feed_offset |
| The offset (delay) to start feeding at the beginning of the simulation, Note that the parameter file uses minutes as the unit. More... | |
| integer, public | global_hours_daytime_feeding |
| Default duration of the day time in hours, night duration is defined as 24 - ::global_hours_day_feeding. Feeding activity occurs only during the day time and not during the night. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_body_mass |
| Fish body mass, g, at the start of the simulation Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_stomach_mass |
| Fish stomach mass, max. filling capacity. Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_midgut_mass |
| Fish mid-gut mass capacity, max. filling capacity. Configuration file example: More... | |
| logical, public | global_stomach_midgut_mass_is_automatic |
| Logical flag that specifies that the stomach and midgut mass (capacity) are automatically recalculated based on the body mass global_body_mass, possibly overriding the parameter values set by global_stomach_mass and global_midgut_mass. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_absorption_ratio |
| Maximum absorption ratio relative to the original dry food item mass. Configuration file example: More... | |
| integer, public | global_ingestion_delay_min |
| Delay of ingestion, min. More... | |
| integer, public | global_digestion_delay_min |
| Delay of digestion, min. It is the delay of absorption after a food item was transmitted to the mid-gut. Any absorption can start only after the digestion delay. Configuration file example: More... | |
| integer, public | global_maximum_duration_midgut_min |
| The maximum duration a food item can be processed in the fish mid-gut, min. If it stays in the mid-gut for any longer time, it is excreted. Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_water_uptake |
| Proportion of water uptake, relative of dry mass of the food item. Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_water_uptake_a |
Parameters of the logistic water uptake function that defines the temporary pattern of water uptake c /(1+a*e**(-r2*t)); where c is the upper limit of the mass, a and r are logistic parameters and e is natural logarithm base. Thus, water uptake dynamics is defined by two additional logistic parameters: Global_Water_Uptake_A and Global_Water_Uptake_R More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_water_uptake_r |
Parameters of the logistic water uptake function that defines the temporary pattern of water uptake c /(1+a*e**(-r2*t)); where c is the upper limit of the mass, a and r are logistic parameters and e is natural logarithm base. Thus, water uptake dynamics is defined by two additional logistic parameters: Global_Water_Uptake_A and Global_Water_Uptake_R More... | |
| integer, public | global_transport_dim |
| Food transport in stomach: Dimensionality of the transport pattern in the stomach. More... | |
| integer, dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_transport_pattern_t |
| Food transport in stomach: Time grid array for interpolation. Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_transport_pattern_r |
| Food transport in stomach: Proportion of food mass left in stomach. Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_temp_factor_midgut_t |
| Temperature adjustment for absorption is controlled by the two parameters below that define the temperature adfjustment grid factor for the Michaelis-Menten equation: global_temp_factor_midgut_t and global_temp_factor_midgut_m This parameter provides the temperature grid for Michaelis-Menten absorption process. More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_stress_factor_hour |
| The pattern of stress effect on the appetite is described by two grid arrays global_stress_factor_hour and global_stress_fact_suppress This global_stress_factor_hour defines the time grid for the stress pattern, h. More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_stress_fact_suppress |
| The pattern of stress effect on the appetite is described by two grid arrays global_stress_factor_hour and global_stress_fact_suppress This global_stress_factor_hour defines the time grid for the stress pattern, h. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_stress_cost_smr |
Maximum value of the metabolic cost of stress in units of resting metabolic rate (SMR). The real metabilic cost scales depending on the time since stress intervention following the stress pattern described by the stress_grid_hour and stress_grid_fact grid. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_stress_activity_decr |
Maximum value of the suppressive effect of stress on baseline activity. The actual suppression of the baseline activity scales depending on the time since stress intervention following the stress pattern described by the stress_grid_hour and stress_grid_fact grid. More... | |
| logical, public | global_stress_intervention_is_minutes |
Global logical flag setting the time unit for the stress intervention parameter array defined by global_stress_intervention_time. If set to TRUE, the stress parameter is set in minutes, otherwise in raw seconds. More... | |
| integer(long), dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_stress_intervention_time |
| The time of stress intervention is set by this array. It is the start points of stressful effects (s). More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_temp_factor_midgut_m |
| Temperature adjustment for absorption is controlled by the two parameters below that define the temperature adfjustment grid factor for the Michaelis-Menten equation: global_temp_factor_midgut_t and global_temp_factor_midgut_m This parameter provides the temperature grid for Michaelis-Menten absorption process. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_transport_baseline_temperature |
| The baseline temperature that applies to the stomach transport pattern defined by global_transport_pattern_t and global_transport_pattern_r. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_transport_baseline_fish_mass |
| The baseline fish mass that applies to the stomach transport pattern defined by global_transport_pattern_t and global_transport_pattern_r. More... | |
| type(stomach_emptying_pattern), public | global_stomach_emptying_pattern |
| Default stomach emptying pattern. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_appetite_fish_night |
| Fish appetite at night. This value is normally low because the fish do not feed at night. If the value is absent or negative, fish appetite does not reduce at night. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_appetite_stomach_threshold |
| Protective appetite threshold for stomach: this is the maximum value of the the_fish::stomach::appetite_stomach() when the overall fish appetite level the_fish::fish::appetite() depends only on stomach filling. Thereby it can protect stomach from overfilling. Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_appetite_logist_a |
| Logistic function parameter A for the appetite factor. See the_fish::appetite_func(). More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_appetite_logist_r |
| Logistic function parameter R for the appetite factor. See the_fish::appetite_func(). More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_mid_gut_mm_r_max |
| Michaelis-Meneten food absorption parameter in mid-gut, | |
| real(srp), public | global_mid_gut_mm_k_m |
| Michaelis-Meneten food absorption parameter in mid-gut, | |
| real(srp), public | global_energy_appetite_rate |
| The steepness parameter of the Logistic energy component of appetite. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_energy_appetite_shift |
| The shift parameter of the Logistic energy component of appetite. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_appetite_activity_factor |
| Activity appetite factor determining how fish locomotor activity increases with increasing appetite. See the_fish::fish_activity_appetite_factor() More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_ue_ze_factor |
| A parameter defining branchial and urine (ZE+UE) energy consumption as a factor to SMR, e.g. 0.3 means (UE+ZE) = 0.3*SMR. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_ue_ze_ammonia_excretion |
| A parameter defining branchial and urine (ZE+UE) energy consumption as a fixed ammonia excretion rate, micro (\mu) mol per g body mass per hour. More... | |
| logical, public | global_is_ue_ze_fixed_rate |
| Logical flag to choose how branchial and urinal (ZE+UE) energy loss is calculated. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_sda_absorp_rate_max |
Defines the specific dynamic action (SDA) that depends on the absorption rate. There are two parameters that define the linear relationship between absorption rate and SDA increase. This parameter defines the maximum absorption rate when the maximum SDA (defined by sda_energy_factor_max) is reached. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_sda_factor_max |
Defines the specific dynamic action (SDA) that depends on the absorption rate. There are two parameters that define the linear relationship between absorption rate and SDA increase. This parameter defines the maximum SDA reached at the maximum absorption rate defined by sda_absorption_rate_max. For example, this parameter equal to 2.0 means that SDA = SMR * 2.0 at the maximum absorption rate. More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_oxygen_grid_x_temp |
| This parameter defines the X axis of the grid: temperature. See commondata::oxygen_rate_std() for details. If the array is not defined in the configuration file, use commondata::trout_oxygen_grid_x_temp Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_oxygen_grid_y_o2std |
| This parameter defines the Y axis of the grid: oxygen consumption. See commondata::oxygen_rate_std() for details. If the array is not defined in the configuration file, use commondata::trout_oxygen_grid_y_o2std Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_food_item_mass |
| Standard mass of one food item. Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_food_gross_energy |
| Gross energy content of the feed, MJ/kg (=kJ7g) Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), parameter, public | min_mass_toler = 0.0001_SRP |
| Minimum mass of food item that counts as non-zero, a tolerance limit. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_temperature |
| Ambient temperature Configuration file example: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_food_input_rate |
| Standard rate of food item input, per minute. Configuration file example: More... | |
| integer, dimension(2), public | global_interval_food_param |
| Parameters of the food provisioning pattern: More... | |
| logical, dimension(:), allocatable, public | global_interval_food_pattern |
| Global food provisioning pattern, logical TRUE/FALSE for each time step. More... | |
| character(len=file_name_len), public | global_food_pattern_file |
| Global variable that keeps the file name for the food provisioning pattern see environ::food_provisioning_get_file() for more details. More... | |
| logical, public | global_food_pattern_file_is_propagate |
| Global logical flag that defines if the feed scheduling pattern defined by the global_interval_food_pattern file will propagate to all 24 h periods or applied just once to the first such period. More... | |
| logical, public | global_food_pattern_file_is_steps |
| Global logical flag that defines if the feed scheduling pattern defined by the global_food_pattern_file file represents the data for each time step (s) (if TRUE) or by minute (FALSE). The default value is FALSE i.e. data are given for each minute. More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_baseline_activity_day |
| Global baseline locomotor activity pattern (swimming speed) for each time step consists of two components: More... | |
| real(srp), public | global_baseline_activity_night |
| real(srp), public | global_feeding_activity_factor |
| Locomotor activity multiplier factor for the activity during the feeding time, i.e. when global_interval_food_pattern is TRUE. More... | |
| character(len=file_name_len), public | global_stats_output_file |
| Global variable keeping the file name for saving general simulation statistics. Data (rows) for each simulation run are normally appended to this file. The data format is CSV. See simulate::model_output_stats_row_csv() for some details. More... | |
| character(len=file_name_len), public | global_stomach_emptying_matrix_file |
| Global variable keeping the file name for the baseline stomach emptying matrix file that keeps the stomach emptying times for fish of different mass and at different temperatures. The file should be prepared in the CSV format and have the following structure: TODO. More... | |
| logical, public | global_output_stats_is_long |
| Define if the output stats are saved using the long or short format. In the first case, both the input parameters and the output stats are saved/appended into the CSV file. Note that the default value is TRUE. More... | |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | def_stats_output_file = "fishmet_stats.csv" |
| Default value of the general simulation statistics file defined in commondata::global_stats_output_file. More... | |
| real(srp), parameter, public | base_e = 2.7182818284590451_SRP |
Natural logarithm base, e More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(*), parameter | trout_oxygen_grid_x_temp = [ 0.0_SRP, 0.5_SRP, 5.0_SRP, 15.2_SRP, 20.1_SRP, 25.2_SRP, 26.2_SRP] |
| Interpolation grid defining the function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the curve from Fig. 9 in Evans, D.O. (1990) Metabolic Thermal compensation by rainbow trout: effects on standard metabolic rate and potential usable power. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 585–600-. More... | |
| real(srp), dimension(*), parameter | trout_oxygen_grid_y_o2std = [38.0_SRP, 38.0_SRP, 40.6_SRP, 67.8_SRP, 94.6_SRP, 136.7_SRP, 145.9_SRP] |
| Interpolation grid defining the function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the curve from Fig. 9 in Evans, D.O. (1990) Metabolic Thermal compensation by rainbow trout: effects on standard metabolic rate and potential usable power. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 585–600-. More... | |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | txt_sec ="s" |
| Time scale abbreviation strings for Y axes of output plots. More... | |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | txt_min ="min" |
| character(len= *), parameter, public | txt_hour ="h" |
Detailed Description
This module defines global parameters and general-level computational utilities.
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ anonymous enum
| anonymous enum |
Definition of time plot scale types for ::global_time_plots_unit_scale.
Definition at line 176 of file m_common.f90.
Function/Subroutine Documentation
◆ model_parameters_txt()
| impure character(len=:) function, allocatable commondata::model_parameters_txt |
Produce a text string containing all global parameters of the model.
Definition at line 834 of file m_common.f90.
◆ is_stress()
| pure logical function commondata::is_stress |
Calculate if stress factor grid is enabled. Stress is disabled if any of the stress parameters are not defined; this includes the stress suppression grid array or the stress intervention array.
Definition at line 1195 of file m_common.f90.
◆ logistic()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::logistic | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | X, |
| real(srp), intent(in) | A, | ||
| real(srp), intent(in) | C, | ||
| real(srp), intent(in) | R | ||
| ) |
◆ michaelis_menten()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::michaelis_menten | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | x, |
| real(srp), intent(in) | r_max, | ||
| real(srp), intent(in) | x50 | ||
| ) |
Michaelis-Meneten function:
![]()
Here ![]() is the maximum rate,
is the maximum rate, ![]() is the Michaelis constant equal to the x at which 1/2 of the maximum rate
is the Michaelis constant equal to the x at which 1/2 of the maximum rate ![]() is reached.
is reached.
gnupolot code:
set xrange [0:1] plot 0.8*x/(0.25+x)
- Parameters
-
[in] x Independent variable. [in] r_max 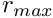 constant.
constant. [in] x50 The Michaelis constant 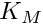 .
.
- Returns
- Output response rate.
Definition at line 1235 of file m_common.f90.
◆ midgut_temp_factor()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::midgut_temp_factor | ( | real(srp), intent(in), optional | temperature | ) |
Calculate temperature adjustment factor for the Michaelis-Menten absorption process in the midgut. The function is based on the cubic spline approcimation using the grid vectors defined by commondata::global_temp_factor_midgut_t and commondata::global_temp_factor_midgut_t.
Definition at line 1254 of file m_common.f90.
◆ feed_energy()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::feed_energy | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | feed_mass, |
| real(srp), intent(in), optional | gross_energy, | ||
| logical, intent(in), optional | is_adjust_water_uptake, | ||
| real(srp), intent(in), optional | water_uptake | ||
| ) |
Calculate the energy content of a feed mass.
- Note
- Units correspondence: mass in kg corresponds to energy in MJ, mass in g corresponds to kJ.
- Parameters
-
[in] feed_mass The mass of the feed, kg [in] gross_energy Gross energy content of the feed, MJ/kg (=kJ/g) [in] is_adjust_water_uptake Optional logical parameter indicating if the energy content of the feed is adjusted for water uptake. If TRUE, the energy content of feed 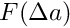 is adjusted by subtracking the water added:
is adjusted by subtracking the water added: 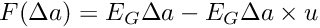 . The default value is TRUE.
. The default value is TRUE. [in] water_uptake Optional water uptake coefficient, if absent, the degault value is taken from global_water_uptake.
- Returns
- Energy content of the input feed mass, MJ
Definition at line 1275 of file m_common.f90.
◆ energy_o2()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::energy_o2 | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | l_o2 | ) |
Calculate the enegretic equivalent (kJ) of Oxygen uptake (l O2) Source: Rønnestad B291.
- Parameters
-
[in] l_o2 Mass of oxygen, l
- Returns
- Energy equivalent, kJ
Definition at line 1325 of file m_common.f90.
◆ o2mass()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::o2mass | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | vol_l | ) |
Calculate the mass of 1 dm3 (l) of Oxygen.
Based on this: 1 mol (22.4l) O2 is 32g, therefore, 1l = 1.43g
- Parameters
-
[in] vol_l Volume of oxygen, l
- Returns
- Mass of oxygen, g
Definition at line 1338 of file m_common.f90.
◆ o2vol()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::o2vol | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | mass_g | ) |
Calculate the volume of 1 dm3 (l) of oxygen.
- Parameters
-
[in] mass_g Mass of oxygen, g
- Returns
- Volume of oxygen, l
Definition at line 1350 of file m_common.f90.
◆ rate2int()
| elemental integer(long) function commondata::rate2int | ( | real(srp), intent(in), optional | rate_min | ) |
The function converts rate per min to interval in seconds.
- Parameters
-
[in] rate_min Optional rate per minute. Default value is set by commondata::global_food_input_rate.
- Returns
- returns interval in seconds between successive events (i.e. every N sec).
The main equation is ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the interval (s) and
is the interval (s) and ![]() is the rate per minute.
is the rate per minute.
Then, to do something every n seconds is implemented as
Definition at line 1362 of file m_common.f90.
◆ cum2rate_int()
| pure real(srp) function, dimension(:), allocatable commondata::cum2rate_int | ( | integer, dimension(:), intent(in) | inarray, |
| integer, intent(in), optional | rate_unit | ||
| ) |
Given an in put array of cumulative sum, this function calculates the rate per unit time defined by the rate_unit argument (as default, per commondata::minute). This requires working on the appropriate difference values for each time interval. Note: This function version accepts integer array.
- Parameters
-
[in] inarray Input Output_Arrays array (integer type) [in] rate_unit Optional rate parameter, the rate is calculated per this number of seconds, the default is per minute
Definition at line 1395 of file m_common.f90.
◆ cum2rate_r()
| pure real(srp) function, dimension(:), allocatable commondata::cum2rate_r | ( | real(srp), dimension(:), intent(in) | inarray, |
| integer, intent(in), optional | rate_unit | ||
| ) |
Given an in put array of cumulative sum, this function calculates the rate per unit time defined by the rate_unit argument (as default, per commondata::minute). This requires working on the appropriate difference values for each time interval. Note: This function version accepts real array (::srp).
- Parameters
-
[in] inarray Input Output_Arrays array (real ::srp type) [in] rate_unit Optional rate parameter, the rate is calculated per this number of seconds, the default is per minute
Definition at line 1436 of file m_common.f90.
◆ blockrate()
| pure real(srp) function, dimension(:), allocatable commondata::blockrate | ( | real(srp), dimension(:), intent(in) | inarray, |
| integer, intent(in), optional | rate_unit | ||
| ) |
Calculate rate based on simple block data, only the block start and end values are considered.
- Note
- This function is used to calculate the growth rate from body size dynamics data.
- Parameters
-
[in] inarray Input Output_Arrays array (real ::srp type) [in] rate_unit Optional rate parameter, the rate is calculated per this number of seconds, the default is per minute
Definition at line 1478 of file m_common.f90.
◆ sgr_blockrate()
|
private |
Calculate an array of specific growth rate rate values based on simple block data,.
- Note
- This function is identical as blockrate() but uses specific growth rate calculated by sgr_i() function. In turn, sgr_i() uses sgr_r() as the backend.
- Parameters
-
[in] inarray Input Output_Arrays array (real ::srp type) [in] rate_unit Optional rate parameter, the rate is calculated per this number of seconds, the default is per minute [in] time_unit Logical flag determining if time in s should be converted to min
Definition at line 1518 of file m_common.f90.
◆ add_to_history_i4()
|
private |
Simple history stack function, add to the end of the stack. We need only to add components on top of the stack and retain commondata::history_size_spatial elements of the prior history (for a spatial moving object). The stack works as follows, assuming 100 and 200 are added:
[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10];
[2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 100];
[3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 100 200].
- Parameters
-
history_array Integer array that keeps the history. add_this we add this element to the end of the history array.
- Note
- This is the integer type version.
Definition at line 1573 of file m_common.f90.
◆ add_to_history_r()
|
private |
Simple history stack function, add to the end of the stack. We need only to add components on top of the stack and retain commondata::history_size_spatial elements of the prior history (for a spatial moving object).
- Parameters
-
history_array Integer array that keeps the history. add_this we add this element to the end of the history array.
- Note
- This is the real type version.
Definition at line 1598 of file m_common.f90.
◆ add_to_history_char()
|
private |
Simple history stack function, add to the end of the stack. We need only to add components on top of the stack and retain commondata::history_size_spatial elements of the prior history.
- Parameters
-
history_array Integer array that keeps the history. add_this we add this element to the end of the history array.
- Note
- This is the character string type version
Definition at line 1622 of file m_common.f90.
◆ last_in_history_r()
|
private |
Return the last value in the array. Note that this function is especially useful for long nested objects, to avoid complex set.
Definition at line 1641 of file m_common.f90.
◆ last_in_history_i4()
|
private |
Return the last value in the array. Note that this function is especially useful for long nested objects, to avoid complex set.
Definition at line 1666 of file m_common.f90.
◆ last_in_history_char()
|
private |
Return the last value in the array. Note that this function is especially useful for long nested objects, to avoid complex set.
Definition at line 1691 of file m_common.f90.
◆ within_r()
|
private |
Force a value within the range set by the vmin and vmax dummy parameter values. If the value is within the range, it does not change, if it falls outside, the output force value is obtained as min( max( value, FORCE_MIN ), FORCE_MAX )
- Parameters
-
[in] value_in Input value for forcing transformation. [in] vmin minimum value of the force-to range (lower limit), if not present, a lower limit of 0.0 is used. [in] vmax maximum value of the force-to range (upper limit)
- Returns
- an input value forced to the range.
- Note
- Note that this is the real precision version of the generic
withinfunction.
Definition at line 1726 of file m_common.f90.
◆ within_i()
|
private |
Force a value within the range set by the vmin and vmax dummy parameter values. If the value is within the range, it does not change, if it falls outside, the output force value is obtained as min( max( value, FORCE_MIN ), FORCE_MAX )
- Parameters
-
[in] value_in Input value for forcing transformation. [in] vmin minimum value of the force-to range (lower limit), if not present, a lower limit of 0.0 is used. [in] vmax maximum value of the force-to range (upper limit)
- Returns
- an input value forced to the range.
- Note
- Note that this is the integer version of the generic
withinfunction.
Definition at line 1758 of file m_common.f90.
◆ oxygen_rate_std_spline()
|
private |
Function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the empirical curve defined by interpolation on the grid determined by two global arrays:
- commondata::global_oxygen_grid_x_temp –
smr_oxygen_temp - commondata::global_oxygen_grid_y_o2std –
smr_oxygen_o2
For rainbow trout, the data are based on Evans, D.O. (1990) Metabolic Thermal compensation by rainbow trout: effects on standard metabolic rate and potential usable power. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 585–600, Fig. 9:
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature ºC | 0.0 | 0.5 | 5.1 | 15.2 | 20.2 | 25.2 | 26.2 |
| SMR | 38.0 | 38.0 | 40.6 | 67.8 | 94.6 | 136.7 | 145.9 |
Interpolation data from Evan 1990:
[0.0 0.5 5.1 15.2 20.2 25.2 26.2] [38.0 38.0 40.6 67.8 94.6 136.7 145.9]
- Note
- Note that this function uses
CSPLINEcubic spline interpolation function fromBASE_UTILS.
- Parameters
-
[in] temperature Temperature Celsius. Note that temperature is an array
- Returns
- Standard Oxygen consumption
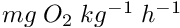 array for the respective input temperatures
array for the respective input temperatures
Definition at line 1805 of file m_common.f90.
◆ oxygen_rate_std_ddpi()
|
private |
Function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the empirical curve defined by interpolation on the grid determined by two global arrays:
- commondata::global_oxygen_grid_x_temp –
smr_oxygen_temp - commondata::global_oxygen_grid_y_o2std –
smr_oxygen_o2
For rainbow trout, the data are based on Evans, D.O. (1990) Metabolic Thermal compensation by rainbow trout: effects on standard metabolic rate and potential usable power. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 585–600, Fig. 9:
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature ºC | 0.0 | 0.5 | 5.1 | 15.2 | 20.2 | 25.2 | 26.2 |
| SMR | 38.0 | 38.0 | 40.6 | 67.8 | 94.6 | 136.7 | 145.9 |
Interpolation data from Evan 1990:
[0.0 0.5 5.1 15.2 20.2 25.2 26.2] [38.0 38.0 40.6 67.8 94.6 136.7 145.9]
- Note
- Note that this function uses
CSPLINE_SCALARcubic splines interpolation function fromBASE_UTILS.
- Parameters
-
[in] temperature Temperature Celsius
- Returns
- Standard Oxygen consumption
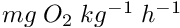
Definition at line 1848 of file m_common.f90.
◆ fcr()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::fcr | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | input_f, |
| real(srp), intent(in) | output_m | ||
| ) |
Function to calculate the FCR, feed conversion rate ![]() .
.
- Parameters
-
[in] input_f Feed mass [in] output_m Body mass increment
- Returns
- Feed conversion rate (FCR)
Definition at line 1862 of file m_common.f90.
◆ kg2g()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::kg2g | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | kg | ) |
Convert kg to g.
Definition at line 1875 of file m_common.f90.
◆ g2kg()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::g2kg | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | g | ) |
Convert g to kg.
Definition at line 1884 of file m_common.f90.
◆ kg2mg()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::kg2mg | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | kg | ) |
Convert kg to mg.
Definition at line 1893 of file m_common.f90.
◆ mg2kg()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::mg2kg | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | mg | ) |
Convert mg to kg.
Definition at line 1902 of file m_common.f90.
◆ mg2g()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::mg2g | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | mg | ) |
Convert mg to g.
Definition at line 1911 of file m_common.f90.
◆ g2mg()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::g2mg | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | g | ) |
Convert g to mg.
Definition at line 1920 of file m_common.f90.
◆ from_micro()
| elemental real(srp) function commondata::from_micro | ( | real(srp), intent(in) | mu_unit | ) |
Convert micro (\mu) unit to unit, e.g. from micro mol to mol Metric prefix micro = 10^-6: unit x 0.000 001.
Definition at line 1930 of file m_common.f90.
◆ sgr_r()
|
private |
Calculates specific growth rate following Houde & Schekter (1981):
![]()
- Note
- Note that this function is the main computation backend that is called in sgr_i() and sgr_blockrate().
- Parameters
-
[in] weight1 Body weight at start of the time interval [in] weight2 Body weight at the end of the time interval [in] time1 Time at the start of the time interval [in] time2 Time at the end of the time interval
Definition at line 1942 of file m_common.f90.
◆ sgr_i()
|
private |
Calculates specific growth rate following Houde & Schekter (1981):
![]()
- Note
- Note that the
is_convert_min(optional) parameter is useful to convert the time step data (s) to min. - Note that this function uses sgr_r() as the backend.
- Parameters
-
[in] weight1 Body weight at start of the time interval [in] weight2 Body weight at the end of the time interval [in] time1 Time at the start of the time interval [in] time2 Time at the end of the time interval [in] time_unit If the two time parameters time1andtime2are provided in raw model time units (s), this parameter allows to rescale these raw units to commondata::minute or commondata::hour.
- Note
- If time units are provided in any other measures than raw time steps (s), this
time_unitparameter should be set to default value or out of normal range (e.g. -1). Then the rate unit will use the same time scale astime1andtime2. Notably, this should ber done if the times are given in commondata::hour.
Definition at line 1963 of file m_common.f90.
◆ stomach_emptying_def_default()
| pure type(stomach_emptying_pattern) function commondata::stomach_emptying_def_default |
Define the default stomach emptying data structure ::stomach_emptying_pattern in case the input data from a CSV file are absent.
Definition at line 2004 of file m_common.f90.
◆ stomach_emptying_txt()
| impure character(len=:) function, allocatable commondata::stomach_emptying_txt | ( | logical, intent(in), optional | is_raw_s | ) |
Show the stomach emptying data structure.
Definition at line 2040 of file m_common.f90.
◆ stomach_transport_txt()
| impure character(len=:) function, allocatable commondata::stomach_transport_txt | ( | real(srp), intent(in), optional | adjust, |
| character(len=*), intent(in), optional | format, | ||
| character(len=*), intent(in), optional | show, | ||
| character(len=*), intent(in), optional | prefix | ||
| ) |
Produce a formatted text string containing the adjusted stomach transport arrays commondata::global_transport_pattern_r and commondata::global_transport_pattern_t.
- Parameters
-
[in] adjust Optional adjustment factor for the array commondata::global_transport_pattern_t [in] format Optional format for the output arrays: "R" for R style, "python" for the Python style, default is the python style. [in] show Default selection of what array to show, transport_pattern_tortransport_pattern_r.[in] prefix Optional prefix string that comes before the array on left.
Definition at line 2101 of file m_common.f90.
Variable Documentation
◆ svn_version_global
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::svn_version_global = '0.1_o' |
Definition at line 31 of file m_common.f90.
◆ program_title
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::program_title = "FishMet: the fish appetite and feeding model" |
Program title that appears on the main interface/window.
Definition at line 34 of file m_common.f90.
◆ is_debug
| logical, parameter, public commondata::is_debug = .TRUE. |
Logical flag that sets the DEBUG mode. When the program is running in the DEBUG mode, additional checks are done and more output is produced.
Definition at line 40 of file m_common.f90.
◆ is_stress_enable
| logical, parameter, public commondata::is_stress_enable = .TRUE. |
Compile-time logical flag that defines if stress effects described by global_stress_factor_hour, global_stress_fact_suppress and global_stress_cost_smr.
Definition at line 45 of file m_common.f90.
◆ debug_warn_level
| real(srp), parameter, public commondata::debug_warn_level = 0.75_SRP |
Warning level in the debugging mode.
Definition at line 48 of file m_common.f90.
◆ label_len
| integer, parameter, public commondata::label_len = 24 |
The default length of labels and similar text strings.
Definition at line 51 of file m_common.f90.
◆ file_name_len
| integer, parameter, public commondata::file_name_len = 255 |
The default length of the file name.
Definition at line 54 of file m_common.f90.
◆ minimum_filename_chars
| integer, parameter, public commondata::minimum_filename_chars = 7 |
The minimum length of a data file. Note that cancelled file name dialog returns a six-char random sequence. Hence the minimum file name > 7.
Definition at line 58 of file m_common.f90.
◆ hour
| integer, parameter, public commondata::hour =3600 |
Global time constants, number of sec in hour and min.
Definition at line 61 of file m_common.f90.
◆ minute
| integer, parameter, public commondata::minute =60 |
Definition at line 61 of file m_common.f90.
◆ max_points_plot
| integer, parameter, public commondata::max_points_plot = 1000 |
The maximum number of data points that are plotted for the model output arrays (squeezed arrays).
Definition at line 65 of file m_common.f90.
◆ is_progress_bar_gui
| logical, parameter, public commondata::is_progress_bar_gui = .TRUE. |
Global parameter defining if progress bar is printed in the GUI mode.
Definition at line 68 of file m_common.f90.
◆ gui_progress_bar_max
| integer, parameter, public commondata::gui_progress_bar_max = 100 |
Maximum value (steps) in the progress bar (minimum is 0)
Definition at line 71 of file m_common.f90.
◆ gui_progress_bar_steps
| integer, parameter, public commondata::gui_progress_bar_steps = 100 |
Number of steps in the progress bar at the GUI mode.
Definition at line 74 of file m_common.f90.
◆ prog_bar_char
| character(len=1), parameter, public commondata::prog_bar_char = "#" |
The symbol used for writing the progress bar in text mode.
Definition at line 77 of file m_common.f90.
◆ prog_bar_len
| integer, parameter, public commondata::prog_bar_len = 42 |
The length of the progress bar in text mode.
Definition at line 80 of file m_common.f90.
◆ crlf
| character, parameter, public commondata::crlf = char(10) |
Definition at line 83 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_time_step
| integer(long), public commondata::global_time_step |
Global variable that defines the current time step.
Definition at line 86 of file m_common.f90.
◆ output_arrays_csv_file
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::output_arrays_csv_file = "model_output_arrays" |
Default file base-name for saving model output arrays.
Definition at line 89 of file m_common.f90.
◆ output_rate_data_csv_file
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::output_rate_data_csv_file = "model_rate_data" |
Default file base-name for saving model rate data.
Definition at line 93 of file m_common.f90.
◆ output_dest_dir
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::output_dest_dir = "" |
Default output directory: all plot and data file will be saved into this directory by default (local directory) unless reconfigured via commondata::global_output_dest.
Definition at line 99 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_output_dest
| character(len=file_name_len), public commondata::global_output_dest |
Output directory: all plot and output files will be saved into this directory, default value is set by output_dest_dir. Specifically, the following outputs are saved to the output_dest directory:
- output plots produced by
savecommand (see if_cmd::cmd_iface_process_commands(), usually set bysetfil()); - output arrays by
save model_output(see simulate::output_arrays_save_csv()); - rate arrays by
save rate_output(see simulate::output_arrays_save_rate_data_csv()); - output statistics by
output statsandappend stats(see if_cmd::cmd_iface_process_commands()).
- Note
- Note that fish object data
save fish_object_datais saved into the commondata::global_fish_object_binary_file exactly as specified in thefish_object_file(commondata::global_fish_object_binary_file) because this is non-human readable internal binary data not intended as the model output. - Note that this parameter affects the program behaviour only in the command line user interface (if_cmd) and not in the graphical user interface (if_gui).
-
Note that the destination can refer to destination directory or output file name prefix. In the former case it should terminate with the operating system specific directory delimiter (e.g.
/on GNU/Linux or/on Microsoft Windows). If the value ofoutput_destdoes not terminate this way, it will refer to the file prefix.
output_dest = "../../../SHARE/data/"
Definition at line 134 of file m_common.f90.
◆ param_file_name_def
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::param_file_name_def = "parameters.cfg" |
Defines the name of the file that keeps global parameters. The parameter file contains the coupled pairs of the parameter name and its value. Comments can be added, normally separated by the # commet symbol.
# Stomach mass of the fish, filling capacity
stomach_capacity = 123.45
# Water uptake, proportional to food item m
water_uptake = 0.1
Definition at line 146 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_param_file_name
| character(len=file_name_len), public commondata::global_param_file_name |
Defines the name of the file that keeps global parameters. This name is normally defined by the environment variable FFA_MODEL_PARAMETER_FILE that is processed in runtime::system_init(). If this environment variable is not set, the parameter file name is defined by the default param_file_name_def.
Definition at line 153 of file m_common.f90.
◆ max_food_items_index
| integer, parameter, public commondata::max_food_items_index = 4000 |
Maximum number of food items in the fish stomach, this is the maximum index for the food items array in the_fish::stomach object.
- Warning
- This index value must always be large enough to ensure maximum filling capacity of the fish stomach global_stomach_mass in units of food items ::Global_Food_Item_Mass given the mass of many food items in the array is diminishing to zero. MAX_FOOD_ITEMS_INDEX >> stomach_capacity / food_item_mass
- Note
- Using a fixed size rather than allocatable array makes it easier to program, faster runtime (less dynamic memory) and reduces stack usage.
Definition at line 168 of file m_common.f90.
◆ verbose
| logical, public commondata::verbose |
Global logical flag to suppress extra text diagnostics and messages, the "quiet mode" or the "verbose mode". If the parameter is TRUE, then verbose mode is activated.
Definition at line 173 of file m_common.f90.
◆ scale_sec
| @, public commondata::scale_sec |
Definition at line 177 of file m_common.f90.
◆ scale_min
| @, public commondata::scale_min |
Definition at line 177 of file m_common.f90.
◆ scale_hour
| @, public commondata::scale_hour |
Definition at line 177 of file m_common.f90.
◆ unscaled
| @, public commondata::unscaled |
Definition at line 177 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_rate_interval
| integer, public commondata::global_rate_interval |
Default rate discretization interval in minutes, this interval is used to plot the ingestion rate.
- Note
- Note that scale types are public.
rate_interval = 10
Definition at line 188 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_run_model_hours
| integer, public commondata::global_run_model_hours |
Default duration of the model run in hours. Note that parameter file uses hours as unit. Conversion to time steps is done in simulate::total_timesteps().
run_model_hours = 24
Definition at line 196 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_day_starts_hour
| integer, public commondata::global_day_starts_hour |
Default hour at which the "daytime" is normally started. This means, in particular, that at the start of the simulation day starts with the offset equal to this parameter value.
day_starts_hour = 4
Definition at line 204 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_run_model_feed_offset
| integer, public commondata::global_run_model_feed_offset |
The offset (delay) to start feeding at the beginning of the simulation, Note that the parameter file uses minutes as the unit.
feed_start_offset = 60
Definition at line 211 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_hours_daytime_feeding
| integer, public commondata::global_hours_daytime_feeding |
Default duration of the day time in hours, night duration is defined as 24 - ::global_hours_day_feeding. Feeding activity occurs only during the day time and not during the night.
daytime_hours = 12
Definition at line 219 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_body_mass
| real(srp), public commondata::global_body_mass |
Fish body mass, g, at the start of the simulation Configuration file example:
body_mass = 200.0
Definition at line 226 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stomach_mass
| real(srp), public commondata::global_stomach_mass |
Fish stomach mass, max. filling capacity. Configuration file example:
stomach_capacity = 24.0
Definition at line 233 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_midgut_mass
| real(srp), public commondata::global_midgut_mass |
Fish mid-gut mass capacity, max. filling capacity. Configuration file example:
midgut_capacity = 24.0
Definition at line 240 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stomach_midgut_mass_is_automatic
| logical, public commondata::global_stomach_midgut_mass_is_automatic |
Logical flag that specifies that the stomach and midgut mass (capacity) are automatically recalculated based on the body mass global_body_mass, possibly overriding the parameter values set by global_stomach_mass and global_midgut_mass.
stomach_midgut_automatic = True
Definition at line 249 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_absorption_ratio
| real(srp), public commondata::global_absorption_ratio |
Maximum absorption ratio relative to the original dry food item mass. Configuration file example:
absorption_ratio = 0.5
Definition at line 257 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_ingestion_delay_min
| integer, public commondata::global_ingestion_delay_min |
Delay of ingestion, min.
- Note
- Note that the model is discrete, with a single time step equivalent to one s Configuration file example:
ingestion_delay = 30
Definition at line 266 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_digestion_delay_min
| integer, public commondata::global_digestion_delay_min |
Delay of digestion, min. It is the delay of absorption after a food item was transmitted to the mid-gut. Any absorption can start only after the digestion delay. Configuration file example:
digestion_delay = 20
Definition at line 275 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_maximum_duration_midgut_min
| integer, public commondata::global_maximum_duration_midgut_min |
The maximum duration a food item can be processed in the fish mid-gut, min. If it stays in the mid-gut for any longer time, it is excreted. Configuration file example:
midgut_maxdur = 180
Definition at line 284 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_water_uptake
| real(srp), public commondata::global_water_uptake |
Proportion of water uptake, relative of dry mass of the food item. Configuration file example:
water_uptake = 0.2
Definition at line 291 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_water_uptake_a
| real(srp), public commondata::global_water_uptake_a |
Parameters of the logistic water uptake function that defines the temporary pattern of water uptake c /(1+a*e**(-r2*t)); where c is the upper limit of the mass, a and r are logistic parameters and e is natural logarithm base. Thus, water uptake dynamics is defined by two additional logistic parameters: Global_Water_Uptake_A and Global_Water_Uptake_R
- Note
- Maxima plot:
wxplot2d( 0.1/(1+200*e**(-0.01*x)), [x,0,1900] );water_uptake_a = 200.0
Definition at line 303 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_water_uptake_r
| real(srp), public commondata::global_water_uptake_r |
Parameters of the logistic water uptake function that defines the temporary pattern of water uptake c /(1+a*e**(-r2*t)); where c is the upper limit of the mass, a and r are logistic parameters and e is natural logarithm base. Thus, water uptake dynamics is defined by two additional logistic parameters: Global_Water_Uptake_A and Global_Water_Uptake_R
- Note
- Maxima plot:
wxplot2d( 0.1/(1+200*e**(-0.01*x)), [x,0,1900] );water_uptake_r = 0.01
Definition at line 315 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_transport_dim
| integer, public commondata::global_transport_dim |
Food transport in stomach: Dimensionality of the transport pattern in the stomach.
Definition at line 319 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_transport_pattern_t
| integer, dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_transport_pattern_t |
Food transport in stomach: Time grid array for interpolation. Configuration file example:
transport_pattern_t = 0 2 8 12
Definition at line 325 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_transport_pattern_r
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_transport_pattern_r |
Food transport in stomach: Proportion of food mass left in stomach. Configuration file example:
transport_pattern_r = 1.0 0.9 0.2 0.0
Definition at line 331 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_temp_factor_midgut_t
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_temp_factor_midgut_t |
Temperature adjustment for absorption is controlled by the two parameters below that define the temperature adfjustment grid factor for the Michaelis-Menten equation: global_temp_factor_midgut_t and global_temp_factor_midgut_m This parameter provides the temperature grid for Michaelis-Menten absorption process.
midgut_temp_fact_t = c(5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 25.0)
Definition at line 342 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stress_factor_hour
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_stress_factor_hour |
The pattern of stress effect on the appetite is described by two grid arrays global_stress_factor_hour and global_stress_fact_suppress This global_stress_factor_hour defines the time grid for the stress pattern, h.
stress_grid_hour = c(0, 10, 20, 40, 50, 72)
Definition at line 352 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stress_fact_suppress
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_stress_fact_suppress |
The pattern of stress effect on the appetite is described by two grid arrays global_stress_factor_hour and global_stress_fact_suppress This global_stress_factor_hour defines the time grid for the stress pattern, h.
stress_grid_fact = c(1.0, 0.9, 0.7, 0.2, 0.1, 0.0)
Definition at line 362 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stress_cost_smr
| real(srp), public commondata::global_stress_cost_smr |
Maximum value of the metabolic cost of stress in units of resting metabolic rate (SMR). The real metabilic cost scales depending on the time since stress intervention following the stress pattern described by the stress_grid_hour and stress_grid_fact grid.
stress_metabolic_cost = 0.5
Definition at line 374 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stress_activity_decr
| real(srp), public commondata::global_stress_activity_decr |
Maximum value of the suppressive effect of stress on baseline activity. The actual suppression of the baseline activity scales depending on the time since stress intervention following the stress pattern described by the stress_grid_hour and stress_grid_fact grid.
stress_inactivity = 0.5
Definition at line 383 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stress_intervention_is_minutes
| logical, public commondata::global_stress_intervention_is_minutes |
Global logical flag setting the time unit for the stress intervention parameter array defined by global_stress_intervention_time. If set to TRUE, the stress parameter is set in minutes, otherwise in raw seconds.
stress_is_min = TRUE
Definition at line 392 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stress_intervention_time
| integer(long), dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_stress_intervention_time |
The time of stress intervention is set by this array. It is the start points of stressful effects (s).
# Two stress events, at 14h and 64h # set in s stress = c(50400, 240400) # set in min stress = c(840, 3840)
Definition at line 403 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_temp_factor_midgut_m
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_temp_factor_midgut_m |
Temperature adjustment for absorption is controlled by the two parameters below that define the temperature adfjustment grid factor for the Michaelis-Menten equation: global_temp_factor_midgut_t and global_temp_factor_midgut_m This parameter provides the temperature grid for Michaelis-Menten absorption process.
midgut_temp_fact_m = c(0.4, 0.6, 1.0, 8.0)
Definition at line 415 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_transport_baseline_temperature
| real(srp), public commondata::global_transport_baseline_temperature |
The baseline temperature that applies to the stomach transport pattern defined by global_transport_pattern_t and global_transport_pattern_r.
transport_pattern_base_temp = 16
Definition at line 422 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_transport_baseline_fish_mass
| real(srp), public commondata::global_transport_baseline_fish_mass |
The baseline fish mass that applies to the stomach transport pattern defined by global_transport_pattern_t and global_transport_pattern_r.
transport_pattern_base_mass = 100
Definition at line 429 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stomach_emptying_pattern
| type(stomach_emptying_pattern), public commondata::global_stomach_emptying_pattern |
Default stomach emptying pattern.
Definition at line 451 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_appetite_fish_night
| real(srp), public commondata::global_appetite_fish_night |
Fish appetite at night. This value is normally low because the fish do not feed at night. If the value is absent or negative, fish appetite does not reduce at night.
appetite_night=0.1
Definition at line 459 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_appetite_stomach_threshold
| real(srp), public commondata::global_appetite_stomach_threshold |
Protective appetite threshold for stomach: this is the maximum value of the the_fish::stomach::appetite_stomach() when the overall fish appetite level the_fish::fish::appetite() depends only on stomach filling. Thereby it can protect stomach from overfilling. Configuration file example:
appetite_threshold_stomach = 0.2
Definition at line 469 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_appetite_logist_a
| real(srp), public commondata::global_appetite_logist_a |
Logistic function parameter A for the appetite factor. See the_fish::appetite_func().
appetite_factor_a = 50000.0
Definition at line 476 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_appetite_logist_r
| real(srp), public commondata::global_appetite_logist_r |
Logistic function parameter R for the appetite factor. See the_fish::appetite_func().
appetite_factor_r = 20.0
Definition at line 483 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_mid_gut_mm_r_max
| real(srp), public commondata::global_mid_gut_mm_r_max |
Michaelis-Meneten food absorption parameter in mid-gut, ![]() (see the_fish::michaelis_menten()) relative to the maximum mass of the food item, rate is per second (basic discrete step of the model).
(see the_fish::michaelis_menten()) relative to the maximum mass of the food item, rate is per second (basic discrete step of the model).
midgut_michaelis_r_max = 0.8
Definition at line 491 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_mid_gut_mm_k_m
| real(srp), public commondata::global_mid_gut_mm_k_m |
Michaelis-Meneten food absorption parameter in mid-gut, ![]() (see the_fish::michaelis_menten()) relative to the total mid-gut mass global_midgut_mass.
(see the_fish::michaelis_menten()) relative to the total mid-gut mass global_midgut_mass.
midgut_michaelis_k = 0.25
Definition at line 499 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_energy_appetite_rate
| real(srp), public commondata::global_energy_appetite_rate |
The steepness parameter of the Logistic energy component of appetite.
appetite_energy_rate = 40.0
Definition at line 505 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_energy_appetite_shift
| real(srp), public commondata::global_energy_appetite_shift |
The shift parameter of the Logistic energy component of appetite.
appetite_energy_shift = 0.2
Definition at line 511 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_appetite_activity_factor
| real(srp), public commondata::global_appetite_activity_factor |
Activity appetite factor determining how fish locomotor activity increases with increasing appetite. See the_fish::fish_activity_appetite_factor()
activity_appetite_factor = 0.5
Definition at line 519 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_ue_ze_factor
| real(srp), public commondata::global_ue_ze_factor |
A parameter defining branchial and urine (ZE+UE) energy consumption as a factor to SMR, e.g. 0.3 means (UE+ZE) = 0.3*SMR.
- Note
- Note that this is the default method.
branchial_energy_factor = 0.3
Definition at line 527 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_ue_ze_ammonia_excretion
| real(srp), public commondata::global_ue_ze_ammonia_excretion |
A parameter defining branchial and urine (ZE+UE) energy consumption as a fixed ammonia excretion rate, micro (\mu) mol per g body mass per hour.
branchial_ammonia_rate = 0.5
Definition at line 535 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_is_ue_ze_fixed_rate
| logical, public commondata::global_is_ue_ze_fixed_rate |
Logical flag to choose how branchial and urinal (ZE+UE) energy loss is calculated.
- If this parameter is TRUE, fixed rate is assumed as defined by global_ue_ze_ammonia_excretion
- if it is FALSE, a fraction of SMR defined by global_ue_ze_factor is used for calculation. This method is the default.
Definition at line 544 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_sda_absorp_rate_max
| real(srp), public commondata::global_sda_absorp_rate_max |
Defines the specific dynamic action (SDA) that depends on the absorption rate. There are two parameters that define the linear relationship between absorption rate and SDA increase. This parameter defines the maximum absorption rate when the maximum SDA (defined by sda_energy_factor_max) is reached.
sda_absorption_rate_max = 0.0007
Definition at line 554 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_sda_factor_max
| real(srp), public commondata::global_sda_factor_max |
Defines the specific dynamic action (SDA) that depends on the absorption rate. There are two parameters that define the linear relationship between absorption rate and SDA increase. This parameter defines the maximum SDA reached at the maximum absorption rate defined by sda_absorption_rate_max. For example, this parameter equal to 2.0 means that SDA = SMR * 2.0 at the maximum absorption rate.
sda_energy_factor_max = 2.0
Definition at line 566 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_oxygen_grid_x_temp
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_oxygen_grid_x_temp |
This parameter defines the X axis of the grid: temperature. See commondata::oxygen_rate_std() for details. If the array is not defined in the configuration file, use commondata::trout_oxygen_grid_x_temp Configuration file example:
smr_oxygen_temp = c(0.0, 0.5, 5.1, 15.2, 20.2, 25.2, 26.2)
Definition at line 576 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_oxygen_grid_y_o2std
| real(srp), dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_oxygen_grid_y_o2std |
This parameter defines the Y axis of the grid: oxygen consumption. See commondata::oxygen_rate_std() for details. If the array is not defined in the configuration file, use commondata::trout_oxygen_grid_y_o2std Configuration file example:
smr_oxygen_o2 = c(38.0, 38.0, 40.6, 67.8, 94.6, 136.7, 145.9)
Definition at line 586 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_food_item_mass
| real(srp), public commondata::global_food_item_mass |
Standard mass of one food item. Configuration file example:
food_item_mass = 2.0
Definition at line 593 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_food_gross_energy
| real(srp), public commondata::global_food_gross_energy |
Gross energy content of the feed, MJ/kg (=kJ7g) Configuration file example:
feed_gross_energy = 23.0
Definition at line 600 of file m_common.f90.
◆ min_mass_toler
| real(srp), parameter, public commondata::min_mass_toler = 0.0001_SRP |
Minimum mass of food item that counts as non-zero, a tolerance limit.
Definition at line 604 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_temperature
| real(srp), public commondata::global_temperature |
Ambient temperature Configuration file example:
temperature = 16.0
Definition at line 611 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_food_input_rate
| real(srp), public commondata::global_food_input_rate |
Standard rate of food item input, per minute. Configuration file example:
food_input_rate = 6.0
Definition at line 618 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_interval_food_param
| integer, dimension(2), public commondata::global_interval_food_param |
Parameters of the food provisioning pattern:
- interval food is provided, min
- interval food is not provided interval, min
These parameters determine the global_interval_food_pattern logical array for each time step.
food_provision_pattern = 10 20
Definition at line 629 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_interval_food_pattern
| logical, dimension(:), allocatable, public commondata::global_interval_food_pattern |
Global food provisioning pattern, logical TRUE/FALSE for each time step.
Definition at line 632 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_food_pattern_file
| character(len=file_name_len), public commondata::global_food_pattern_file |
Global variable that keeps the file name for the food provisioning pattern see environ::food_provisioning_get_file() for more details.
- Note
- Note that the file has priority over the food provisioning pattern defined in global_interval_food_param.
food_provision_file_name = "../zzz.csv"
Definition at line 641 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_food_pattern_file_is_propagate
| logical, public commondata::global_food_pattern_file_is_propagate |
Global logical flag that defines if the feed scheduling pattern defined by the global_interval_food_pattern file will propagate to all 24 h periods or applied just once to the first such period.
food_provision_file_repeat = TRUE
Definition at line 649 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_food_pattern_file_is_steps
| logical, public commondata::global_food_pattern_file_is_steps |
Global logical flag that defines if the feed scheduling pattern defined by the global_food_pattern_file file represents the data for each time step (s) (if TRUE) or by minute (FALSE). The default value is FALSE i.e. data are given for each minute.
food_provisioning_file_by_s = FALSE
Definition at line 658 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_baseline_activity_day
| real(srp), public commondata::global_baseline_activity_day |
Global baseline locomotor activity pattern (swimming speed) for each time step consists of two components:
- baseline that differs at day global_baseline_activity_day and night global_baseline_activity_night
- feeding activity increment defined by feeding activity factor global_feeding_activity_factor
This is illustrated by the following diagram:
+----+ feeding activity multiplier
| |
+--+ - -+----------------+
| | baseline
-------------------+ +-------------------> activity
-night-------------+-day--------------------+-night------------->see the_fish::fish_activity_baseline() for more details.
baseline_activity_day = 4.0 baseline_activity_night = 0.5
Definition at line 685 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_baseline_activity_night
| real(srp), public commondata::global_baseline_activity_night |
Definition at line 685 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_feeding_activity_factor
| real(srp), public commondata::global_feeding_activity_factor |
Locomotor activity multiplier factor for the activity during the feeding time, i.e. when global_interval_food_pattern is TRUE.
Definition at line 690 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stats_output_file
| character(len=file_name_len), public commondata::global_stats_output_file |
Global variable keeping the file name for saving general simulation statistics. Data (rows) for each simulation run are normally appended to this file. The data format is CSV. See simulate::model_output_stats_row_csv() for some details.
stats_output_file = fishmet_stats.csv
Definition at line 699 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_stomach_emptying_matrix_file
| character(len=file_name_len), public commondata::global_stomach_emptying_matrix_file |
Global variable keeping the file name for the baseline stomach emptying matrix file that keeps the stomach emptying times for fish of different mass and at different temperatures. The file should be prepared in the CSV format and have the following structure: TODO.
stomach_emptying_matrix = fishmet_stom_data.csv
Definition at line 710 of file m_common.f90.
◆ global_output_stats_is_long
| logical, public commondata::global_output_stats_is_long |
Define if the output stats are saved using the long or short format. In the first case, both the input parameters and the output stats are saved/appended into the CSV file. Note that the default value is TRUE.
stats_output_long = TRUE
Definition at line 718 of file m_common.f90.
◆ def_stats_output_file
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::def_stats_output_file = "fishmet_stats.csv" |
Default value of the general simulation statistics file defined in commondata::global_stats_output_file.
Definition at line 722 of file m_common.f90.
◆ base_e
| real(srp), parameter, public commondata::base_e = 2.7182818284590451_SRP |
Natural logarithm base, e
Definition at line 725 of file m_common.f90.
◆ trout_oxygen_grid_x_temp
| real(srp), dimension(*), parameter commondata::trout_oxygen_grid_x_temp = [ 0.0_SRP, 0.5_SRP, 5.0_SRP, 15.2_SRP, 20.1_SRP, 25.2_SRP, 26.2_SRP] |
Interpolation grid defining the function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the curve from Fig. 9 in Evans, D.O. (1990) Metabolic Thermal compensation by rainbow trout: effects on standard metabolic rate and potential usable power. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 585–600-.
Interpolation data from Evan 1990:
[0.0 0.5 5.1 15.2 20.2 25.2 26.2] \ [38.0 38.0 40.6 67.8 94.6 136.7 145.9]
This parameter defines the X axis of the grid: temperature. See commondata::oxygen_rate_std() for details.
Definition at line 743 of file m_common.f90.
◆ trout_oxygen_grid_y_o2std
| real(srp), dimension(*), parameter commondata::trout_oxygen_grid_y_o2std = [38.0_SRP, 38.0_SRP, 40.6_SRP, 67.8_SRP, 94.6_SRP, 136.7_SRP, 145.9_SRP] |
Interpolation grid defining the function calculating standard oxygen consumption in rainbow trout based on the curve from Fig. 9 in Evans, D.O. (1990) Metabolic Thermal compensation by rainbow trout: effects on standard metabolic rate and potential usable power. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 585–600-.
Interpolation data from Evan 1990:
[0.0 0.5 5.1 15.2 20.2 25.2 26.2] \ [38.0 38.0 40.6 67.8 94.6 136.7 145.9]
This parameter defines the Y axis of the grid: oxygen consumption. See commondata::oxygen_rate_std() for details.
Definition at line 760 of file m_common.f90.
◆ txt_sec
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::txt_sec ="s" |
Time scale abbreviation strings for Y axes of output plots.
Definition at line 764 of file m_common.f90.
◆ txt_min
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::txt_min ="min" |
Definition at line 764 of file m_common.f90.
◆ txt_hour
| character(len=*), parameter, public commondata::txt_hour ="h" |
Definition at line 764 of file m_common.f90.